การนำมาประยุกต์ใช้งาน
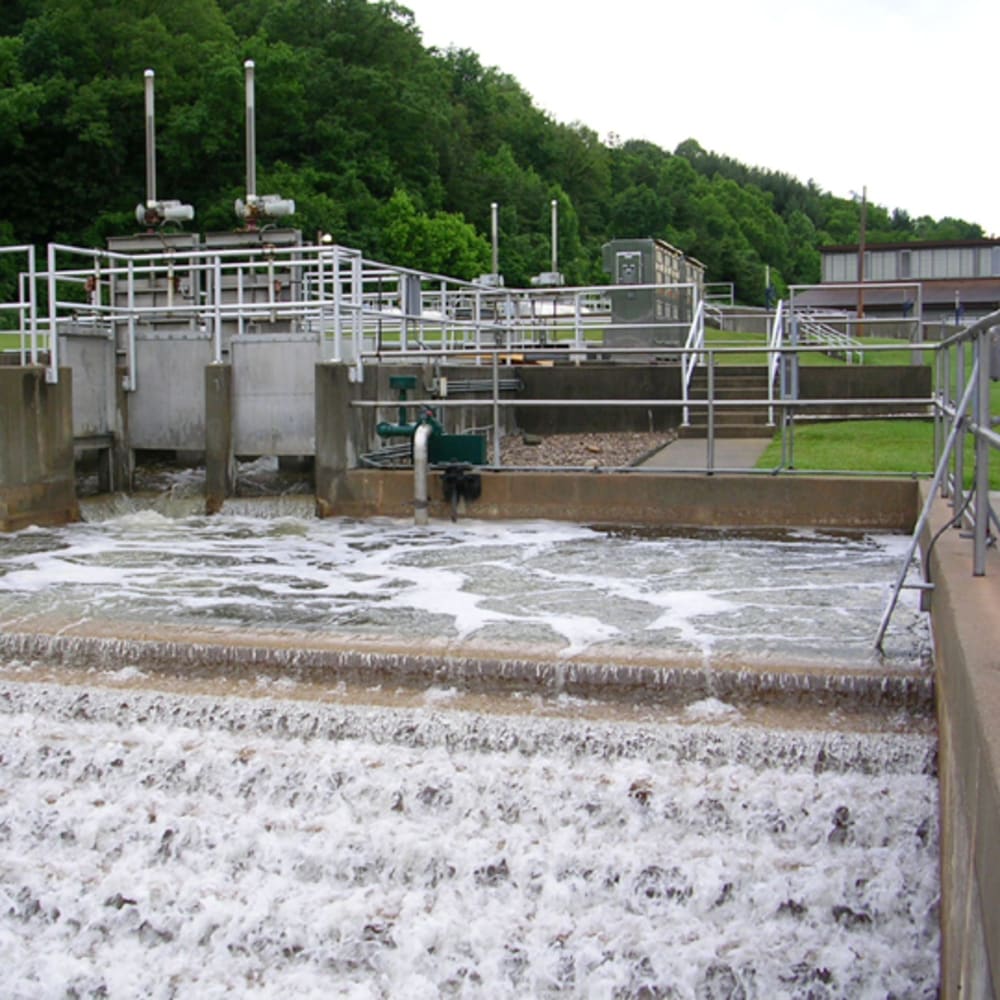
TKN determination in water and wastewater
SpeedDigester K-439, Kjel Line and MultiDist: Steam distillation and Potentiometric determination of Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) according to the Kjeldahl method in water and wastewater along with determination of Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ).
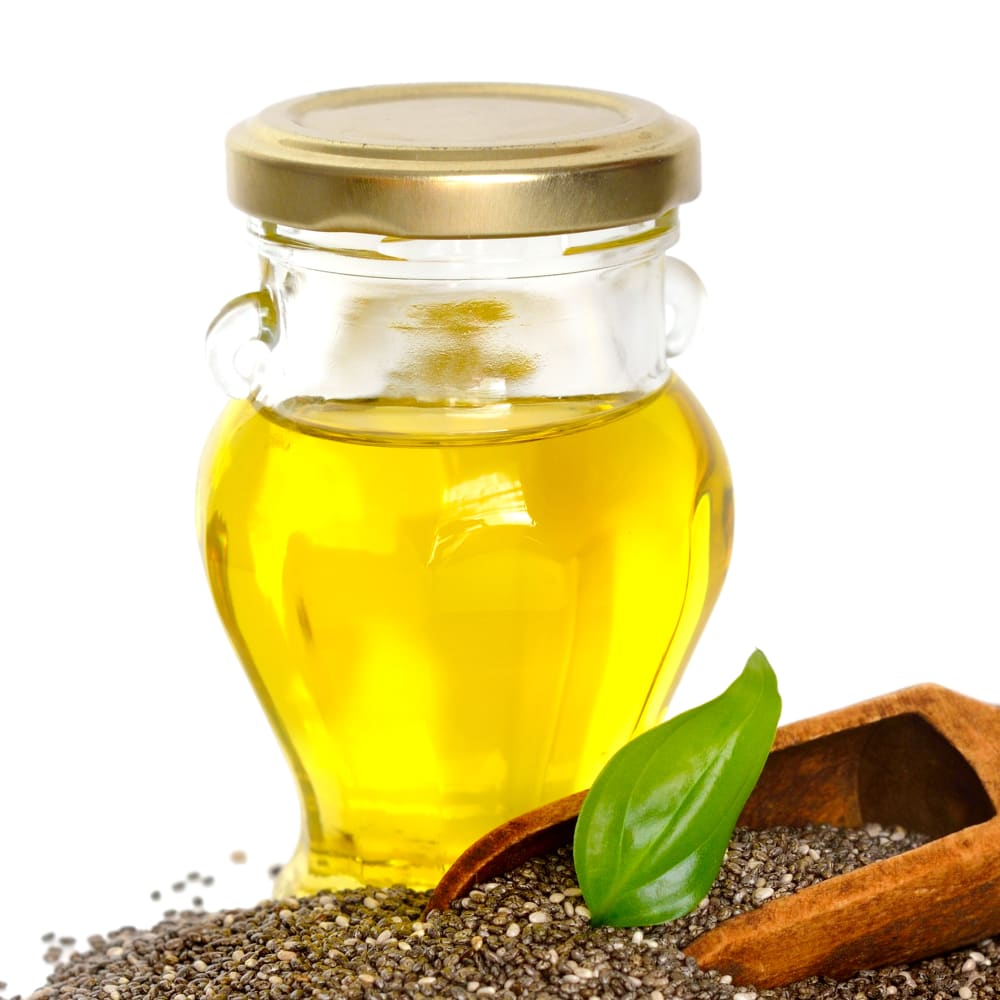
Determination of oil contents in seed samples
SpeedExtractor E-916, Multivapor, Hydrolysis Unit E-416, Extraction Unit E-816 SOX: Comparison of different extraction methods: Pressurized Solvent Extraction (PSE) using SpeedExtractor E-916 versus Weibull Stoldt method using Hydrolysis Unit E-416 and Extraction Unit E-816 SOX
Determination of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers and chloro substituted benzene congeners in air
Syncore® Analyst R-12, Residual volume 1.0 mL, Vacuum Pump V-300, Interface I-300 Pro, Recirculating Chiller F-314, Flushback module R-12: Time saving concentration and reproducible recovery rates of volatile analytes.