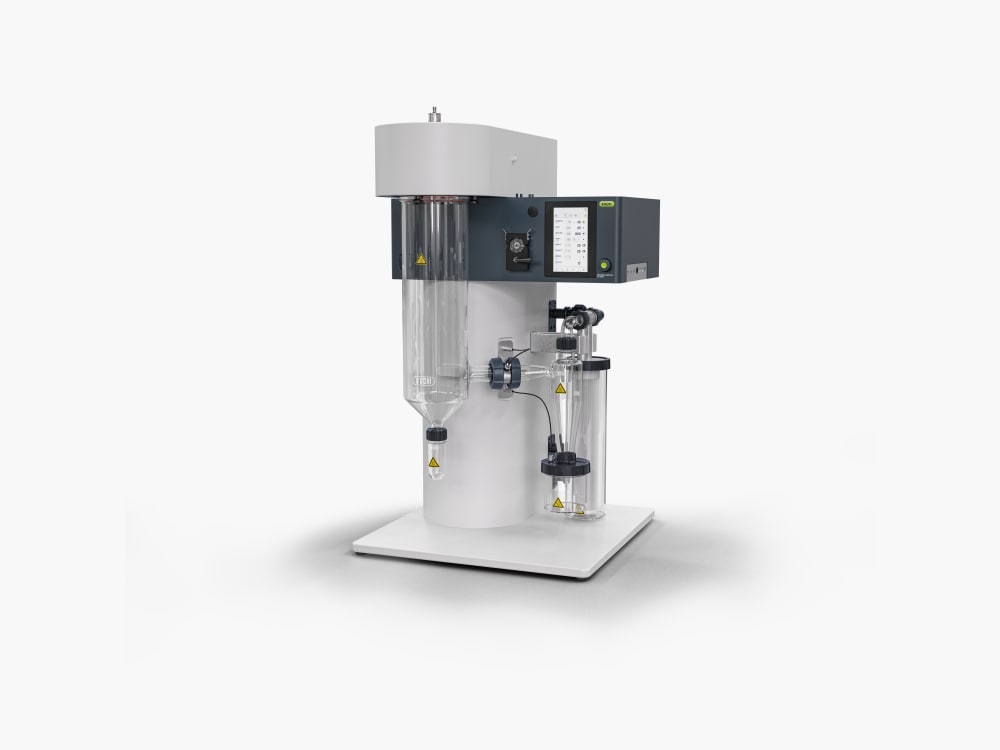
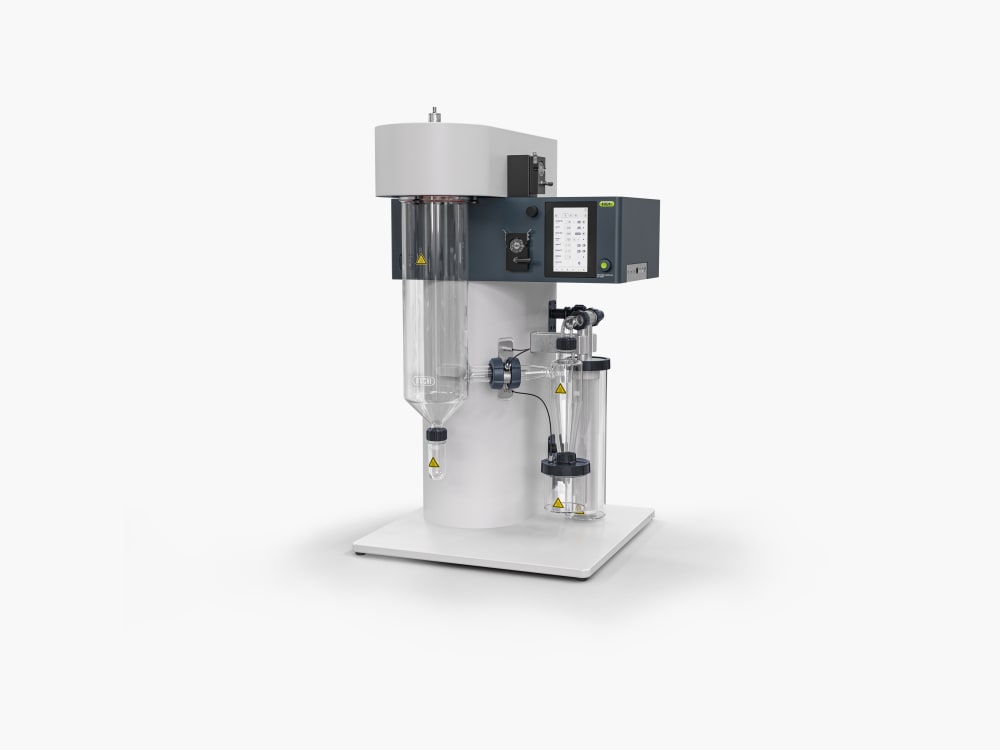
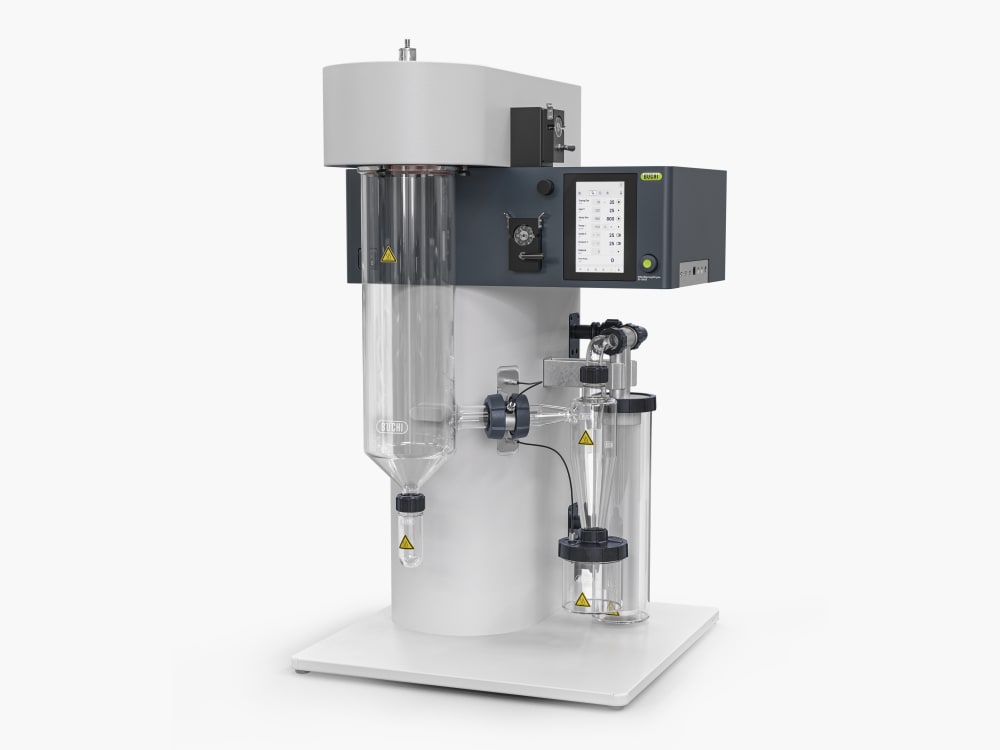
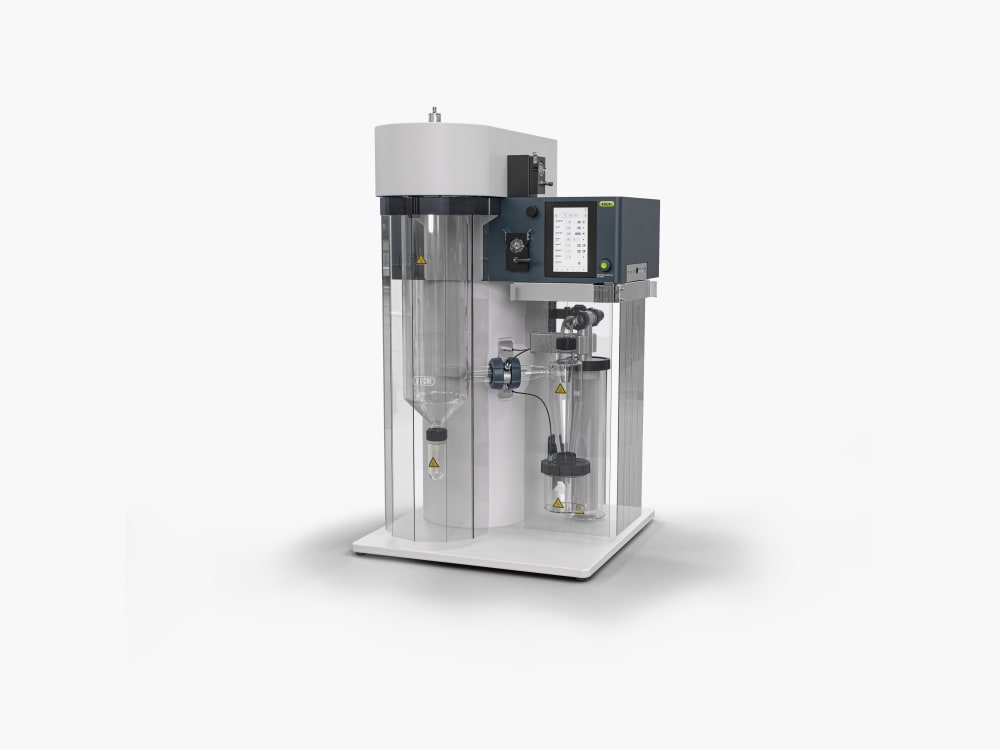
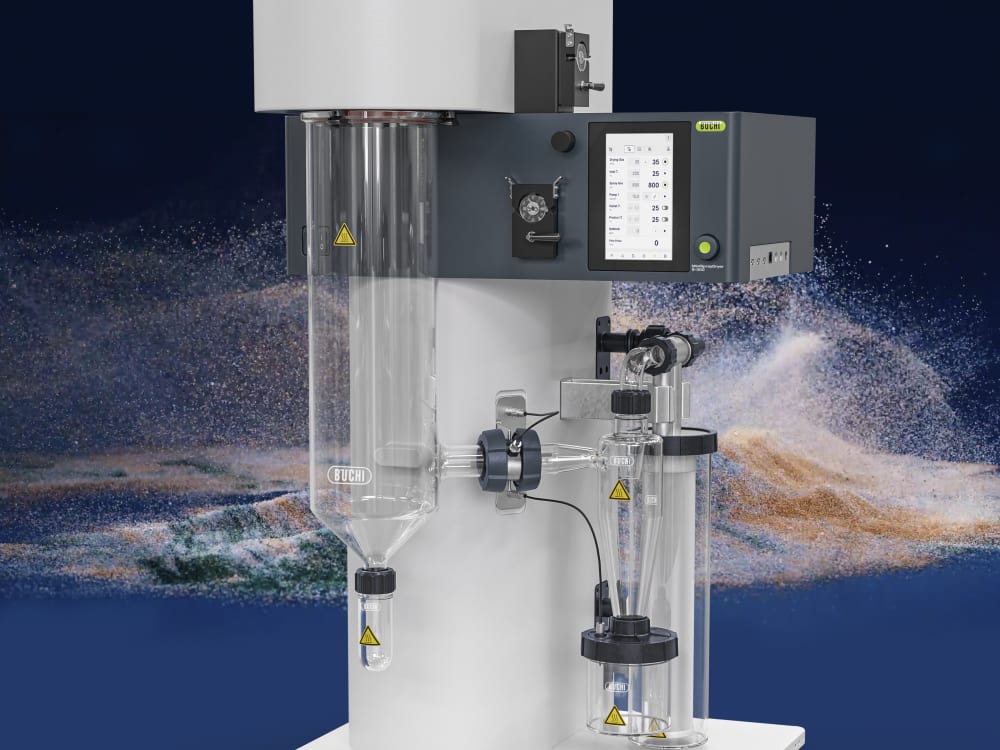
Mini Spray Dryer S-300
The next generation laboratory spray dryer
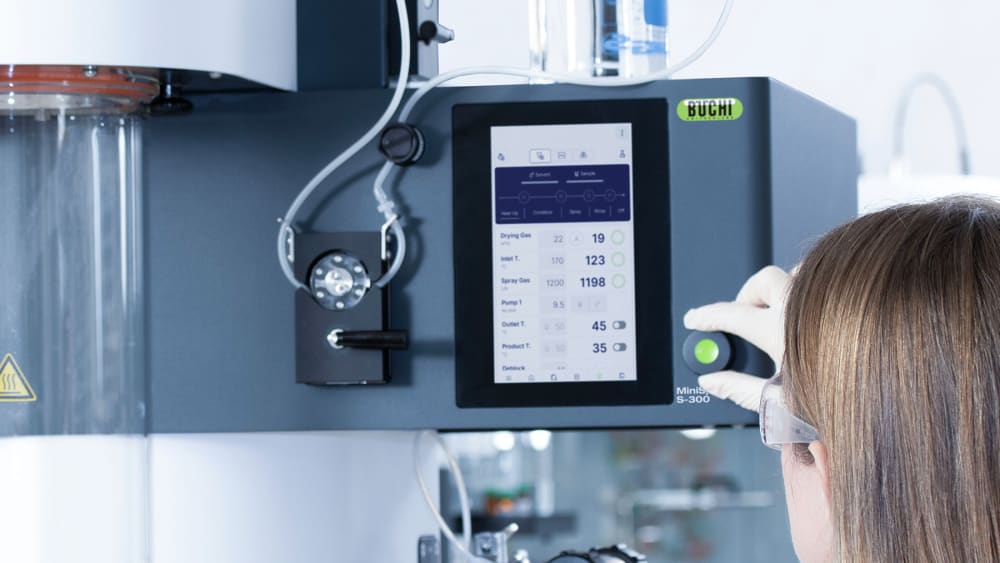
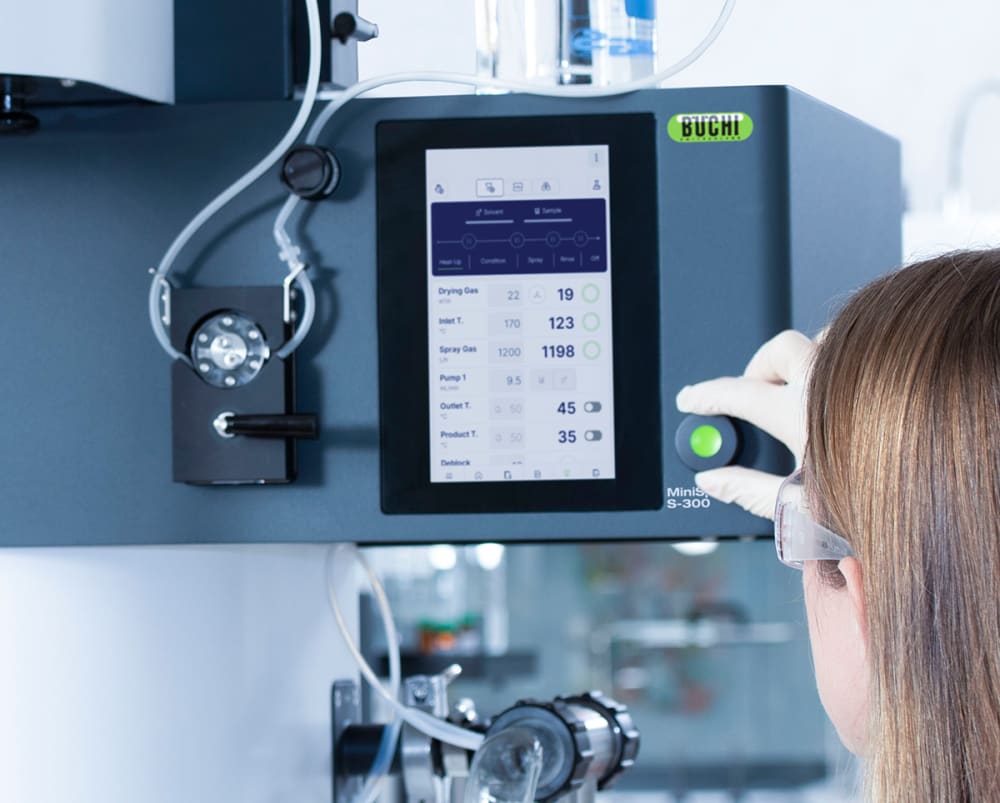
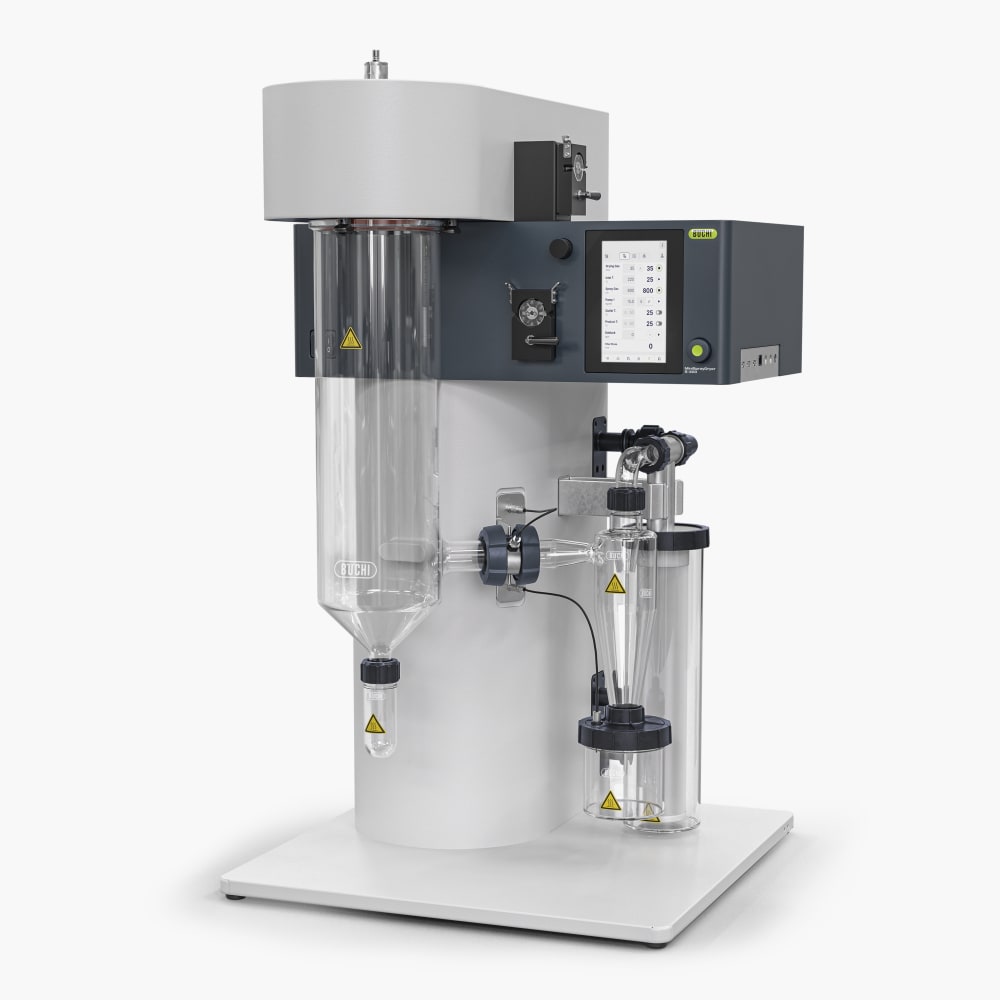
With the Mini Spray Dryer S-300, BUCHI solidifies its position as a global market leader for more than 40 years. The laboratory spray dryer combines outstanding product design with unique instrument capabilities to offer a superior user experience.

Features
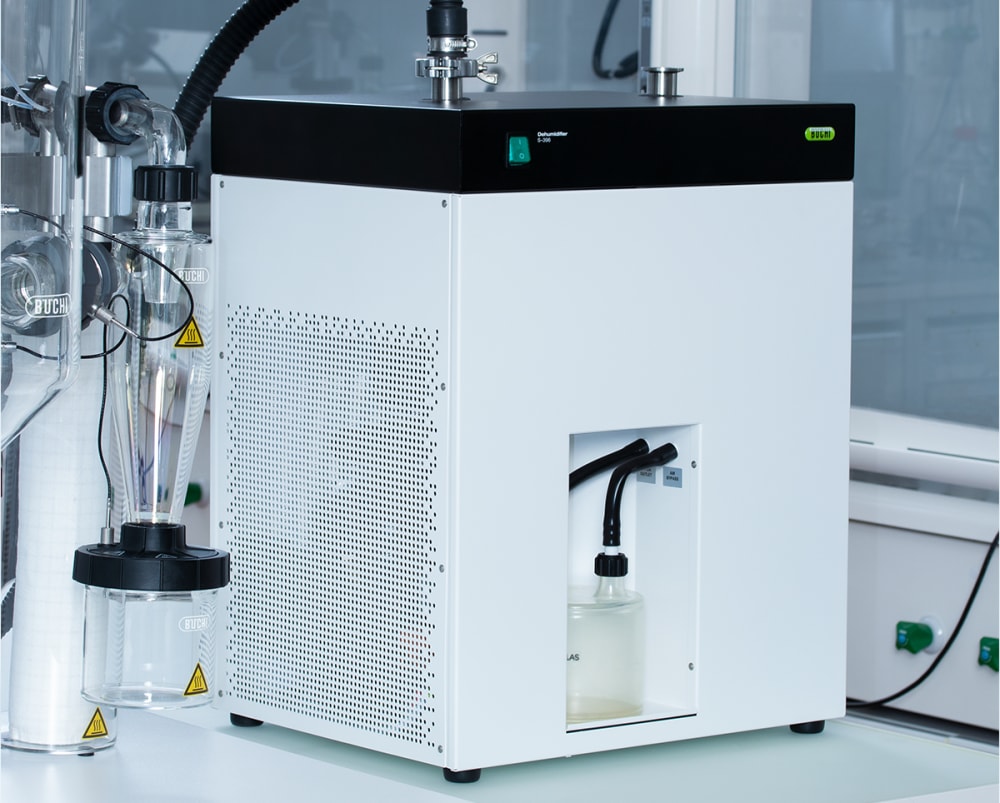
In combination with the Inert Loop S-395, the Mini Spray Dryer S-300 allows for the safe handling of samples with organic solvents. The nitrogen drying gas is circulated and the solvent is collected as condensate. For your safety, the oxygen level and gas flow in the system are continuously monitored.
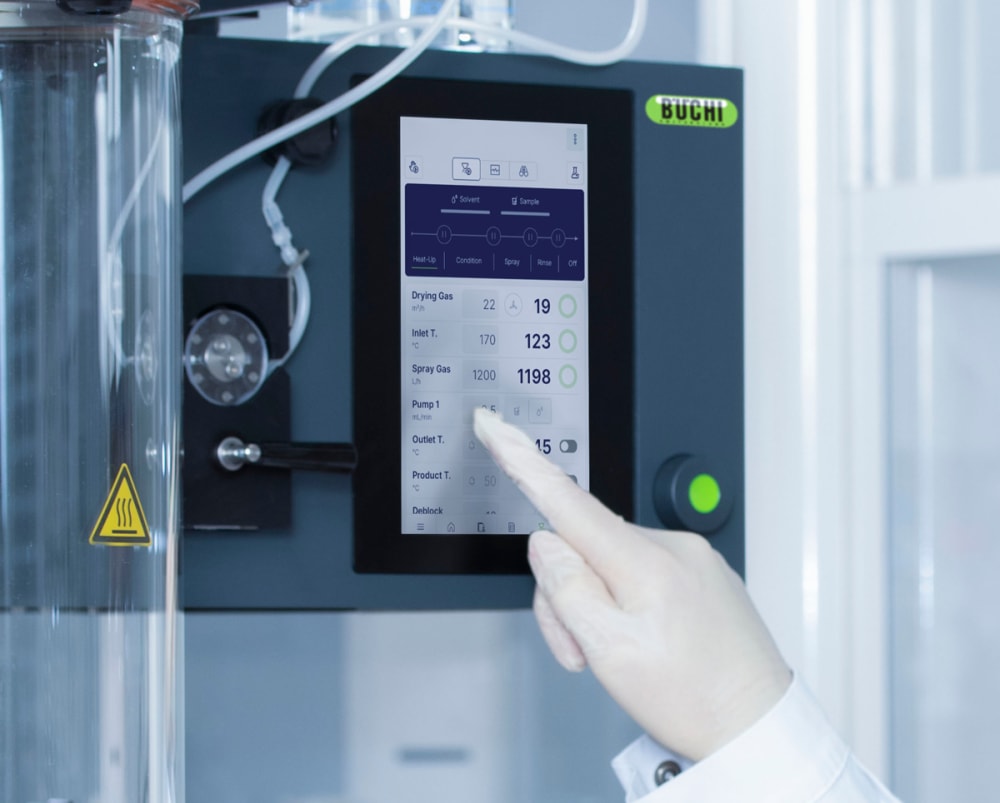
The Auto Mode allows you to program your Mini Spray Dryer S-300 Advanced and run your method automatically. The instrument will heat up, condition the outlet temperature, spray pure solvent, spray your sample, spray pure solvent again and shut down after the sample is processed. The auto mode improves the time efficiency of your process, especially during repetitive tasks.
All parameters in the Mini Spray Dryer S-300, such as spraying gas, drying gas and pump speed, are provided in SI values and are automatically regulated by the system. These features maximize the reproducibility of your process.
Control or monitor the Mini Spray Dryer S-300 from anywhere at any time. The app on any mobile device or computer grants you full access to the entire user interphase of the system. With remote control options, you gain flexible time management and fast reaction times to process alterations.
Save time and hassle by saving your runs as methods and repeating them later. You can also program a sample queue to run one sample after another on your Mini Spray Dryer S-300 for added convenience.
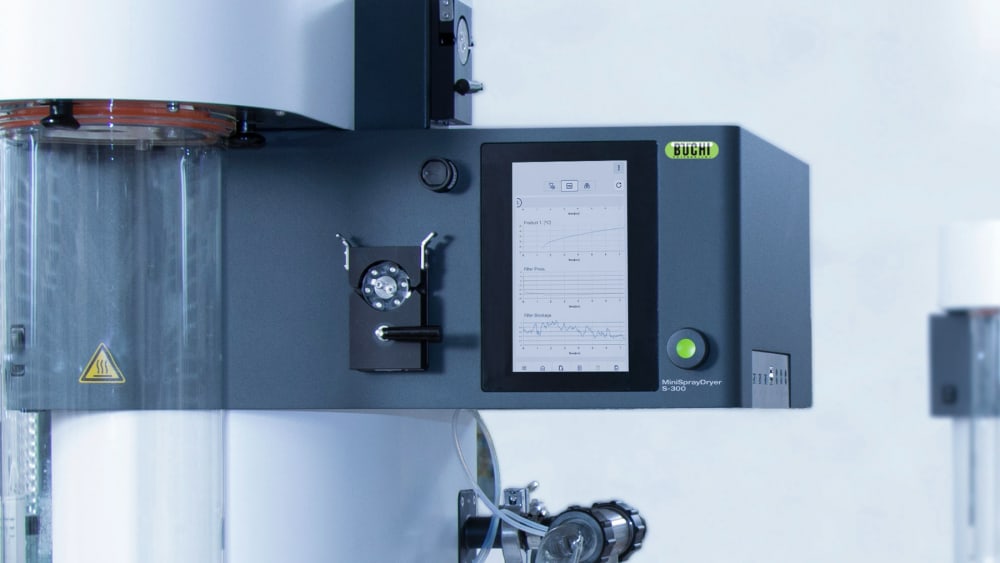
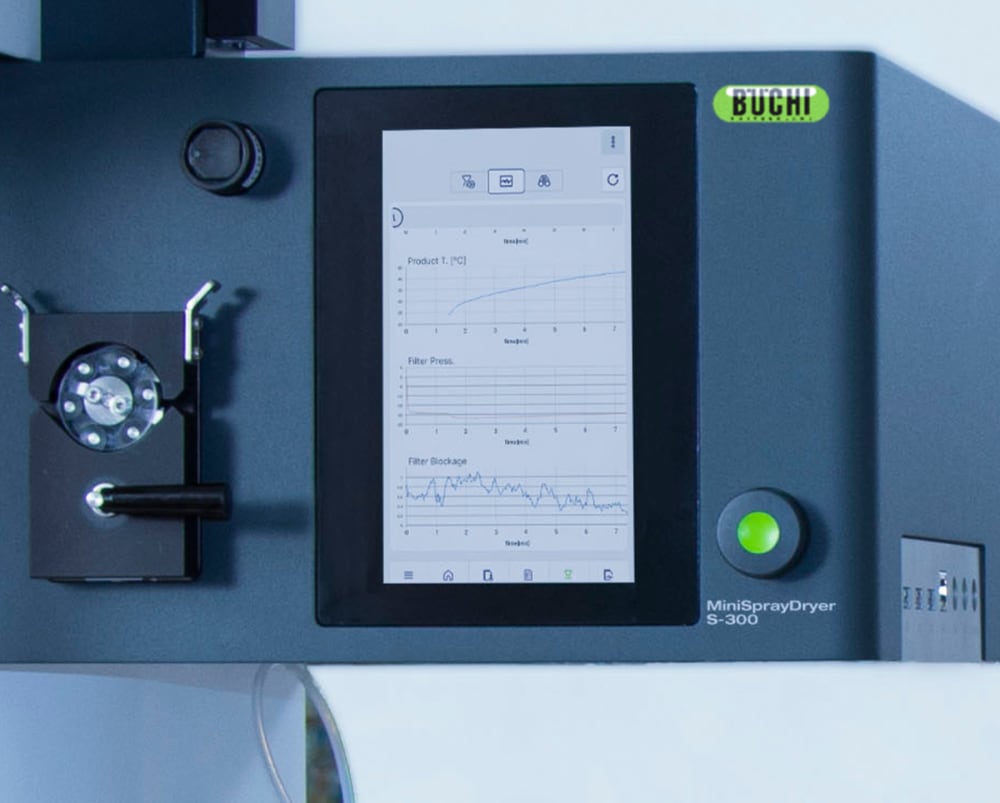
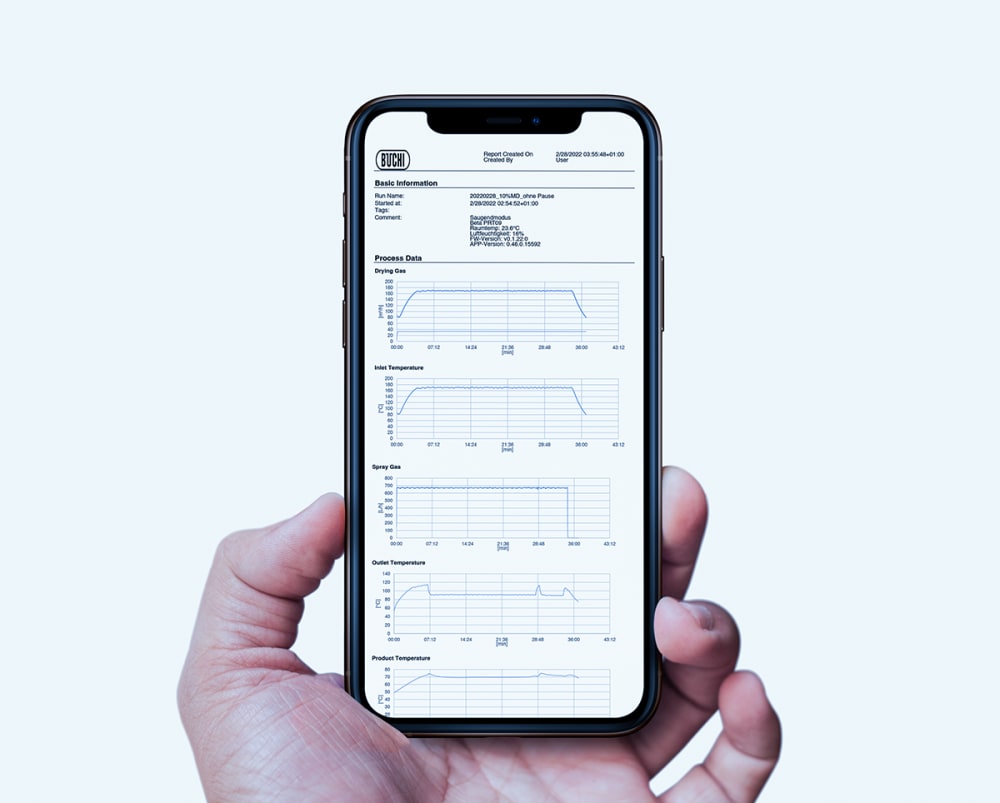
All the runs you perform on the Mini Spray Dryer S-300 are recorded and saved on the instrument. With the push of a button, you can easily generate a PDF report or a .csv file with your process data.
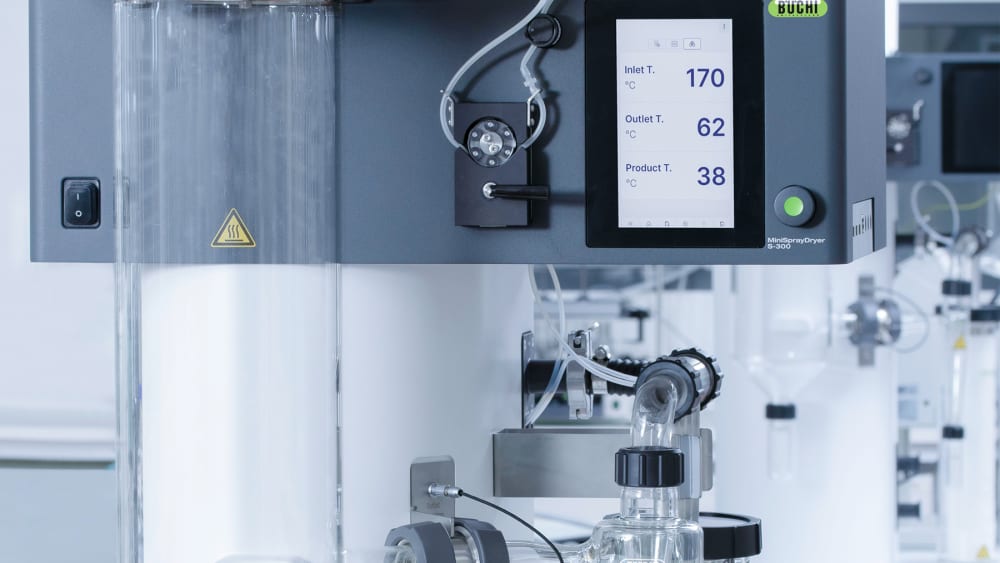
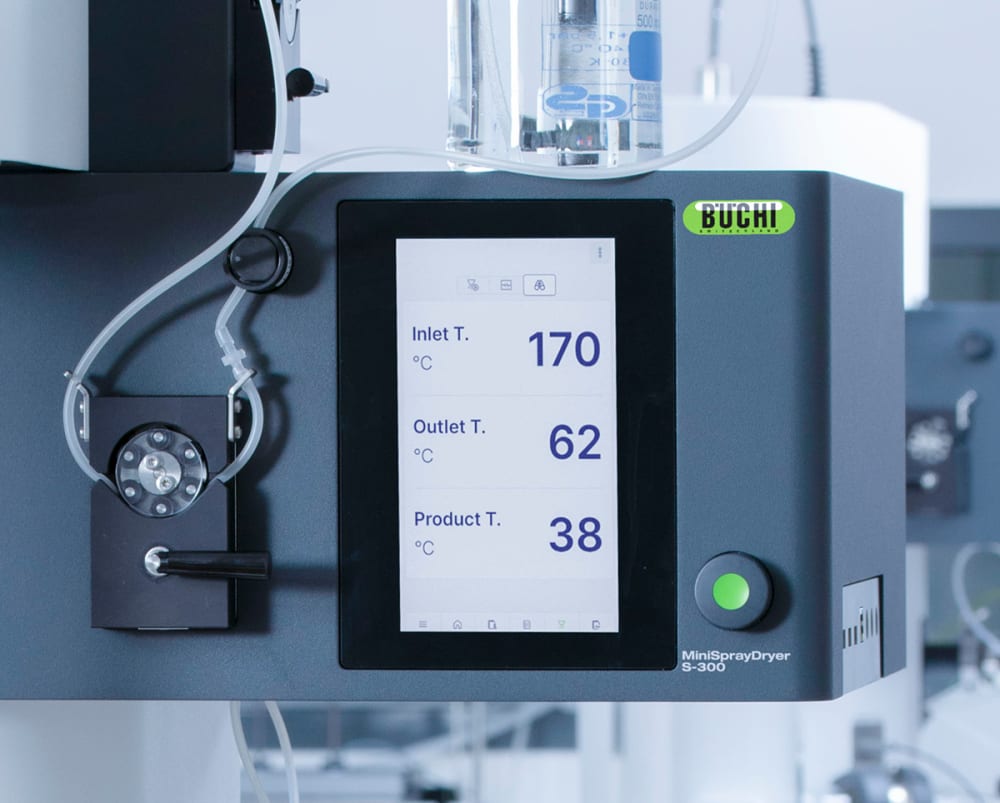
To give you more information about the thermal influences on your sample, the Mini Spray Dryer S-300 allows you to monitor both the outlet temperature and the final product temperature. This information can help you better protect your samples, especially when spray drying heat sensitive samples.
Reduce sample loss during lab spray drying thanks toa cyclone with a conductive coating that reduces the ability of your sample to stick to the walls.
With more than 40 years of experience in laboratory scale spray drying, BUCHI has accumulated vast application know-how.. Find one of the thousands of publications with BUCHI spray dryers in scientific libraries or explore our online Spray Drying application database to find applications that match your needs.
With the Mini Spray Dryer S-300, you can reproduce the results that you achieved with older models of the BUCHI Mini Spray Dryer. You will not lose any of you valuable work for a quick, seamless transfer to the new instrument.
Compare the Mini Spray Dryer S-300
Related Parts & Accessories
Downloads
- Operation Manual Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
- Technical Data Sheet Mini Spray Dryer S-300(pdf)
- Product Brochure Mini Spray Dryer S-300 en(pdf)
Related Instruments
Related Courses & Trainings
Applications
Unmatched flexibility for a full range of applications
Pharma
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a vital process in the pharmaceutical industry, used for the formulation and development of various drugs and medications. It involves converting liquid solutions or suspensions into dry powders through atomization and rapid evaporation. This technique offers several benefits, including improved stability, enhanced bioavailability, and ease of handling. In recent years, several notable trends have emerged in laboratory-scale spray drying within the pharmaceutical sector. One significant trend is the use of spray drying for the production of solid dispersions. Solid dispersions are formulations where the drug is dispersed in a solid matrix, enhancing its solubility and dissolution rate. Spray drying enables the preparation of solid dispersion powders with uniform drug distribution, leading to improved drug delivery and efficacy. Another trend is the development of inhalable drugs using spray drying. This technique allows for the production of dry powder formulations suitable for inhalation, facilitating targeted delivery to the respiratory system. Inhalable drugs offer advantages in the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Taste masking is another important application of laboratory-scale spray drying. By encapsulating drugs with unpleasant taste profiles in taste-masking particles, the palatability of oral formulations can be improved. Spray drying enables the encapsulation of drugs within taste-masking coatings, leading to better patient compliance, particularly for pediatric and geriatric populations. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying is increasingly employed for the development of controlled-release formulations. By incorporating drugs into sustained-release matrices or encapsulating them within microspheres or nanoparticles, spray drying allows for the controlled release of drugs over an extended period. This enables optimized drug dosage regimens and improved patient convenience. In conclusion, laboratory-scale spray drying in the pharmaceutical area is witnessing several significant trends, including the production of solid dispersions, inhalable drugs, taste-masking formulations, and controlled-release systems. These trends contribute to the development of novel drug formulations with enhanced solubility, targeted delivery, improved patient compliance, and optimized drug release profiles.
Chemicals / Materials
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of materials in the chemicals and materials science field. In recent years, notable trends have emerged, including the application of spray drying for nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. One trend is the use of laboratory-scale spray drying in the synthesis of nano materials. This technique enables the production of nanoparticles and nanostructured materials with controlled size, morphology, and composition. By tailoring these properties, researchers can develop advanced materials with improved mechanical strength, enhanced conductivity, and tailored surface functionalities. Spray drying also finds application in the production of paints and coatings. By producing fine and uniform particles, spray drying contributes to the desired properties of coatings, such as improved color, durability, and film formation. This trend leads to the development of high-quality coatings with enhanced performance and functionality. Furthermore, laboratory-scale spray drying plays a role in the development of catalysts. By controlling particle size, composition, and surface area, spray drying allows for the design and optimization of catalysts for efficient chemical transformations and environmental applications. In summary, laboratory-scale spray drying in the chemicals and materials science field is witnessing trends in nano materials, paints and coatings, and catalysts. These trends contribute to the development of advanced materials, high-performance coatings, and efficient catalysts, driving innovation in various industries.
Batteries
Laboratory-scale spray drying is a valuable technique in battery research for the fabrication of electrode materials. It enables precise control over particle size and morphology, resulting in electrodes with optimized electrochemical performance. Spray drying allows for the production of fine and uniform particles, contributing to the development of high-performance batteries. This method facilitates the development of electrode materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity and electrochemical stability. By employing laboratory-scale spray drying in battery research, scientists can advance energy storage technologies and develop more efficient and reliable batteries for various applications.
Food
Applications: Encapsulation of additives, controlled release, nutraceuticals, functional foods, flavors, vitamins, proteins, probiotic bacteria, juice concentrate, milk powder Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Biotech
Applications: Cells, bacteria and protein encapsulation, cell transplantation, biotransformation Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization, Cell encapsulation Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Nano Spray Dryer B-90, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300
Cosmetics
Applications: Cosmetics, fragrances Methods: Drying, encapsulation of liquids, Encapsulation of solids, Micronization Instruments used: Mini Spray Dryer S-300, Encapsulator B-390 / B-395, Lyovapor L-200 / L-300